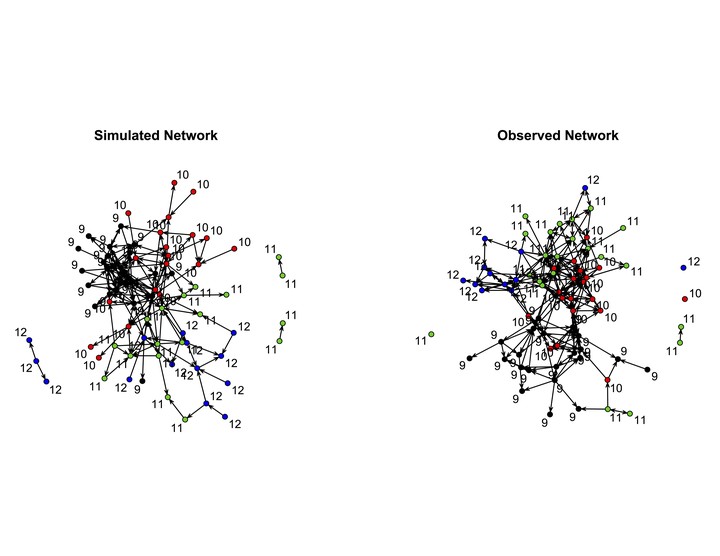
Abstract
Random graphs, where the connections between nodes are considered random variables, have wide applicability in the social sciences. Exponential-family Random Graph Models (ERGM) have shown themselves to be a useful class of models for representing complex social phenomena. We generalize ERGM by also modeling nodal attributes as random variates, thus creating a random model of the full network, which we call Exponential-family Random Network Models (ERNM). We demonstrate how this framework allows a new formulation for logistic regression in network data. We develop likelihood-based inference for the model and an MCMC algorithm to implement it. This new model formulation is used to analyze a peer social network from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. We model the relationship between substance use and friendship relations, and show how the results differ from the standard use of logistic regression on network data.