Abstract
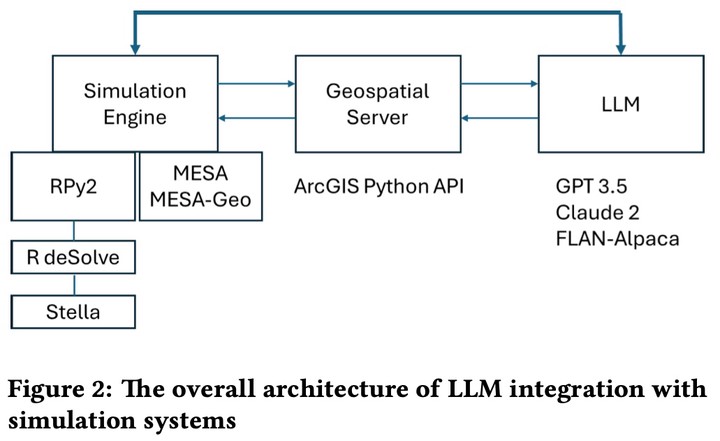
We present our experience integrating large language models (LLMs) and simulation engines to enhance spatially-disaggregated simulation, taking advantage of the spatial knowledge and spatial reasoning capabilities of LLMs. The examples illustrate LLM integration with different variations of compartmental epidemiological models, including agent-based models (ABM) in the context of modeling COVID-19 infection spread in a school setting, and LLM integration with a system dynamics model which supports a serious game focused on strategies for responding to disease outbreaks at the county level. We present the architecture of the integrated LLM-simulation system, demonstrate the initial results, and discuss the challenges of the current approach, related to LLM’s understanding of spatial information and spatial relationships, their reasoning capabilities, and model performance and scalability.