A Framework for the Comparison of Maximum Pseudo Likelihood and Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Exponential Family Random Graph Models
Abstract
The statistical modeling of social network data is difficult due to the complex dependence structure of the tie variables. Statistical exponential families of distributions provide a flexible way to model such dependence. They enable the statistical characteristics of the network to be encapsulated within an exponential family random graph (ERG) model. For a long time, however, likelihood-based estimation was only feasible for ERG models assuming dyad independence. For more realistic and complex models inference has been based on the pseudo-likelihood. Recent advances in computational methods have made likelihood-based inference practical, and comparison of the different estimators possible.
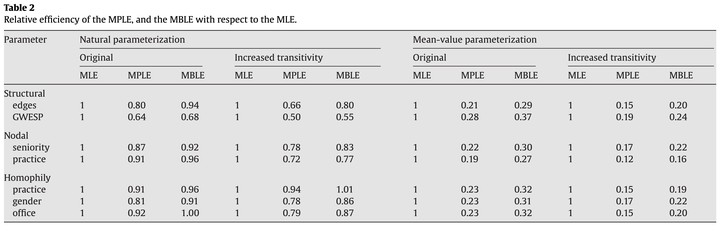
In this paper, we present methodology to enable estimators of ERG model parameters to be compared. We use this methodology to compare the bias, standard errors, coverage rates and efficiency of maximum likelihood and maximum pseudo-likelihood estimators. We also propose an improved pseudo-likelihood estimation method aimed at reducing bias. The comparison is performed using simulated social network data based on two versions of an empirically realistic network model, the first representing Lazega’s law firm data and the second a modified version with increased transitivity. The framework considers estimation of both the natural and the mean-value parameters.
The results clearly show the superiority of the likelihood-based estimators over those based on pseudo-likelihood, with the bias-reduced pseudo-likelihood out-performing the general pseudo-likelihood. The use of the mean-value parameterization provides insight into the differences between the estimators and when these differences will matter in practice.